Directory Localizer API
Changes in Directory Localizer API Specification Document
Changes in Directory Localizer API
Purpose
The purpose of Directory Localizer API is to offer the functions
for making directory localization.
API description
Directory Localizer API is a library API, which provides an interface
class to utilize directory localization. With directory localization,
a localized name and a specified icon are combined with a directory.
For example, the image folder is shown as “Image”, but its full path
may be
C:\\Data\\Images\\
.
Use cases
The most common use cases of Directory Localizer API are the following:
-
Defining Directory Localizer in a resource file
-
Initializing Directory Localizer
-
Retrieving the localized attributes of a directory
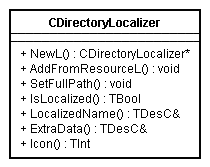
API class structure
The main classes of Directory Localizer API are shown in the figure
below.
The class
CDirectoryLocalizer
is derived from
CBase
.
The class
CDirectoryLocalizer
is used to instantiate
the Directory Localizer instance by reading the resource and make
the localization for an absolute path.
Directory Localizer resource and directory resource
A Directory Localizer resource contains an array of directory resources.
The following table gives a detailed description of the fields in
a directory resource.
|
|
|
|
LTEXT fullPath
|
Full path of the directory.
|
|
LTEXT localizedName
|
Localized name.
|
|
LTEXT extraData
|
Extra data, for example localized name for another layout.
|
|
WORD iconIndex
|
Index of an icon.
|
Related APIs
-
CBase
-
CDirectoryLocalizer
Using Directory Localizer API
The most common use cases are described in the sections below.
Defining Directory Localizer in a resource file
Clients can use the default localization data provided with the
Symbian platform, or define a new one in a resource file. An example
Directory Localizer containing two directory resources is shown as
below:
#include "DirectoryLocalizer.rh"
RESOURCE DIRECTORYLOCALIZER r_example_localizer_entries
{
directories =
{
DIRECTORY
{
fullPath = “c:\\example\\”;
localizedName = “Example”;
extraData = “New localizer”;
iconIndex = 0;
},
DIRECTORY
{
fullPath = “c:\\example2\\”;
localizedName = “Example2”;
extraData = “New localizer 2”;
iconIndex = 0;
}
};
}
Initializing Directory Localizer
Directory Localizer may be initialized with the default localizer
resource, or a client specified resource. The following code snippet
demonstrates how to initialize a localizer with the resource defined
in the above section.
// Assumption: the localizer resource is defined in resource file “example.rss”.
//
#include <example.rsg>
_LIT(KDLExampleResourceFile, "z:\\resource\\example.rsc" );
// Load the resource file to the environment.
//
TInt offsetRscFile = CCoeEnv::Static()->
AddResourceFileL(KDLExampleResourceFile);
// Initialize the localizer with the resource.
//
CDirectoryLocalizer* localizer = NULL;
localizer = CDirectoryLocalizer::NewL( R_EXAMPLE_LOCALIZER_ENTRIES );
// Handle the localized data.
...
// Delete the instance.
//
delete localizer;
localizer = NULL;
// Delete the resource file from the envionment.
//
CCoeEnv::Static()->DeleteResourceFile(offsetRscFile);
The following code snippet demonstrates how to add specified localizer
resource to the default localizer resource entries. In this case,
a localizer is initialized with the default localizer entries firstly,
and then calling
CDirectoryLocalizer::AddFromResourceL()
method adds the resource defined in the above section.
// Assumption: the localizer resource is defined in resource file “example.rss”.
//
#include <example.rsg>
_LIT(KDLExampleResourceFile, "z:\\resource\\example.rsc" );
// Load the resource file to the environment.
//
TInt offsetRscFile = CCoeEnv::Static()->
AddResourceFileL(KDLExampleResourceFile);
// Initialize the localizer with the default resource.
//
CDirectoryLocalizer* localizer = NULL;
localizer = CDirectoryLocalizer::NewL();
// Add resource entries.
//
localizer->AddFromResourceL(R_EXAMPLE_LOCALIZER_ENTRIES);
// Handle the localized data.
...
// Delete the instance.
//
delete localizer;
localizer = NULL;
// Delete the resource file from the envionment.
//
CCoeEnv::Static()->DeleteResourceFile(offsetRscFile);
Related APIs
-
CDirectoryLocalizer::AddFromResourceL()
Retrieving the localized attributes of a directory
The most important use case is to analyze an absolute path and
retrieve the localized attributes, e.g. the localized name. The following
code snippet demonstrates how to retrieve the localized attributes
of the path defined in
KTestDir
.
// Assumption: CDirectoryLocalizer* localizer has been initialized as described
// in the section “Initializing the directory localizer”.
//
// Define the input path.
//
_LIT( KTestDir, "c:\\example\\" );
// Set the absolute path to be localized.
//
localizer ->SetFullPath(KTestDir);
if ( localizer->IsLocalized() )
{
// The path is recognized as a localized directory.
// Get the localized name. It should be “Example”
// If the input path is not localized, the return value is KNullDesC.
//
TPtrC localizeName = localizer-> LocalizedName();
// Get the extra data. It should be “New localizer”
// If the input path is not localized, the return value is KNullDesC.
//
TPtrC extraData = localizer-> ExtraData ();
// Get the icon index. It should be 0.
// If the input path is not localized, the return value is KErrGeneral.
//
TInt iconIndex = localizer-> Icon ();
}
The path to be localized is defined with or without the trailing
backslash depending on how the paths are defined in the directory
resource. And the default localizer entries are defined with the trailing
backslash. So it is recommended to define the path with the trailing
backslash as the resource defined in section
Defining the directory localizer in a resource file
.
Related APIs
Error handling
Some methods may leave, for example if running out of memory. Normal
Symbian error handling practices should be used, including
e.g. using cleanup stack and
TRAP
harness.
Related APIs