Connection Monitor Server API
Changes in Connection Monitor Server API documentation
Changes
The following header file(s) have changed between S60 3rd Edition and
S60 5th Edition.
rconnmon.h
|
New constant
|
|
|
|
New constant
|
|
const TUint KBearerGroupThreshold;
Used by GetUintAttribute,
SetUintAttribute.
|
|
New constant
|
|
const TUint KBearerGroupInfo;
Used by GetPckgAttribute.
|
|
New constant
|
|
const TUint KWlanNetworks;
Used by GetPckgAttribute.
|
|
New constant
|
|
const TUint KWlanScanCacheLifetime;
Used by GetIntAttribute,
SetIntAttribute.
|
|
New constant
|
|
const TUint KWlanScanMaxDelay;
Used by GetUintAttribute,
SetUintAttribute.
|
|
New constant
|
|
const TUint KWlanSsid;
Used by GetStringAttribute,
SetStringAttribute.
|
|
New constant
|
|
const TUint KWlanSsidNetworks;
Used by GetPckgAttribute.
|
|
New constant
|
|
const TUint KWlanCurrentNetwork;
Used by GetPckgAttribute.
|
|
New constant
|
|
const TUint KWlanProbeRawBuffers;
Used by GetPckgAttribute.
|
|
New enumeration
|
|
enum TConnMonBearerInfo;
|
|
New enumeration
|
|
enum TConnMonBearerGroup;
|
|
New enumeration value
|
|
TConnMonEvent::EConnMonBearerInfoChange
|
|
New enumeration value
|
|
TConnMonEvent::EConnMonBearerGroupChange
|
|
New class
|
TConnMonBearerGroupInfo
|
class TConnMonBearerGroupInfo
|
|
New class
|
CConnMonBearerInfoChange
|
NONSHARABLE_CLASS( CConnMonBearerInfoChange ) : public CConnMonEventBase
|
|
New class
|
CConnMonBearerGroupChange
|
NONSHARABLE_CLASS( CConnMonBearerGroupChange ) : public CConnMonEventBase
|
|
New class
|
CConnMonWlanNetwork
|
NONSHARABLE_CLASS( CConnMonWlanNetwork ): public CBase
|
|
New class
|
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg
|
class CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg : public CBase
|
|
New class
|
CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffer
|
NONSHARABLE_CLASS( CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffer ) : public CBase
|
|
New class
|
CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffersPckg
|
class CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffersPckg : public CBase
|
|
New type definition
|
|
typedef TPckgBuf<TConnMonBearerGroupInfo> TConnMonBearerGroupInfoBuf;
|
|
New type definition
|
|
typedef RPointerArray<CConnMonWlanNetwork> RConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArray;
|
|
New type definition
|
|
typedef RPointerArray<CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffer> RConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffersPtrArray;
|
Related APIs
-
CConnMonBearerGroupChange
-
CConnMonBearerInfoChange
-
CConnMonWlanNetwork
-
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg
-
CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffer
-
CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffersPckg
-
TConnMonBearerGroupInfo
-
TConnMonEvent::EConnMonBearerGroupChange
-
TConnMonEvent::EConnMonBearerInfoChange
Purpose
Connection Monitor Server provides an API for applications to get information
about active data connections and other data connection related information
like connection method availability and WLAN information. Client applications
can receive this information via requests and events. Connection Monitor Server
API also provides a way to close any connection or all connections. This document
describes Connection Monitor Server API.
Constraints
This API is valid for all platforms running on Symbian OS v9.3 or later.
Classification and release information
Connection Monitor Server API is an SDK API.
This document is valid from S60 5th Edition.
Emulator support
This API is supported in the WINS/WINSCW emulator environment, with the
following exceptions:
API description
The Connection Monitor Server API is a server-client API, that is, an active
object-based implementation encapsulating a client-server session interface.
The API is defined in
rconnmon.h
and the library is
connmon.lib
.
Use cases
The main use cases of Connection Monitor Server API are:
-
Connecting and disconnecting.
-
Getting basic connection level information.
-
Cancelling a request.
-
Stopping a connection.
-
Registering for events.
-
Catching events.
-
Using TInt attributes.
-
Using TUint attributes.
-
Using TBool attributes.
-
Using string attributes.
-
Using packaged attributes.
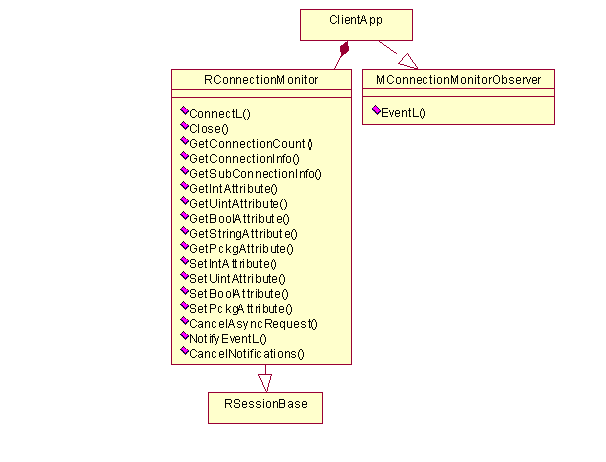
API class structure
The following diagram shows the Connection Monitor Server interface class
structure.
Clients can access Connection Monitor Server by creating an object from
the
RConnectionMonitor
class. This class is derived from
RSessionBase
and
it provides methods for retrieving and setting attribute values from/to Connection
Monitor Server.
In order to get notifications from Connection Monitor Server, an application
needs to implement the
MConnectionMonitorObserver
class and
its pure virtual
EventL
method. The Connection Monitor Server
API calls this method when an event occurs. Different events are implemented
as classes and all of them have a common base class.
Related APIs
-
EventL
-
MConnectionMonitorObserver
-
RConnectionMonitor
-
RSessionBase
Using the Connection Monitor Server API
The client application first instantiates the
RConnectionMonitor
class.
Then it can access all API methods. If the client application wants to listen
to notifications, it must implement the
MConnectionMonitorObserver
class
and register an instance of it to the API. Most of the API calls are asynchronous
and can be cancelled.
Connecting and disconnecting
For simplicity, the instance of
RConnectionMonitor
is
an automatic variable in the example below. When the instance of
RConnectionMonitor
is
a member variable,
ConnectL()
should be called when constructing
the object and
Close()
should be called when destructing.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
// Open RConnectionMonitor object
monitor.ConnectL();
// ...
// Close RConnectionMonitor object when it is not needed any more
monitor.Close();
Related APIs
-
Close()
-
ConnectL()
-
RConnectionMonitor
Getting basic connection level information
The following example shows how to retrieve various connection level information.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
TUint connectionCount( 0 );
TUint subConnectionCount( 0 );
TUint connectionId( 0 );
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Get connection count
monitor.GetConnectionCount(
connectionCount,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
if ( connectionCount == 0 ) { /* No connection */ }
// Get connection info (1st connection)
TInt error = monitor.GetConnectionInfo(
1,
connectionId,
subConnectionCount );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { // Error }
TBuf<KConnMonMaxStringAttributeLength> iapName;
TUint iapId = 0;
TUint downlinkData = 0;
TUint uplinkData = 0;
TInt signalStrength = 0;
TBool connectionActivity = EFalse;
TInt bearer = 0;
TBuf<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KMaxNameLength> ssid;
TUint transmitPower = 0;
TInt networkMode = 0;
TInt securityMode = 0;
TBuf<KConnMonMaxStringAttributeLength> apName;
// Get connection IAP name
monitor.GetStringAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KIAPName,
iapName,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get connection IAP ID
monitor.GetUintAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KIAPId,
iapId,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get connection downlink data (in bytes)
monitor.GetUintAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KDownlinkData,
downlinkData,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get connection uplink data (in bytes)
monitor.GetUintAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KUplinkData,
uplinkData,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get the signal strength (in mW)
monitor.GetIntAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KSignalStrength,
signalStrength,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get the current connection activity
monitor.GetBoolAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KConnectionActive,
connectionActivity,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get the connection bearer
monitor.GetIntAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KBearer,
bearer,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
if ( bearer == EBearerWLAN )
{
// Get ssid name
monitor.GetStringAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KNetworkName,
ssid,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get WLAN transmit power
monitor.GetUintAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KTransmitPower,
transmitPower,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get network mode
monitor.GetIntAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KNetworkMode,
networkMode,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get security mode
monitor.GetIntAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KSecurityMode,
securityMode,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
}
else
{
// Get access point name
monitor.GetStringAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KAccessPointName,
apName,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
}
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Cancelling a request
The following example shows how to cancel an outstanding ConnMon request.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
TInt error( KErrNone );
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Buffer for WLAN information
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg* wlanBuf =
new( ELeave ) CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg( 2048 );
TPtr wlanPtr( wlanBuf->Buf()->Des() );
// Set a 120 second WLAN scan delay
TUint scanDelay = 120;
error = monitor.SetUintAttribute(
EBearerIdWLAN,
0,
KWlanScanMaxDelay,
scanDelay );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Request a WLAN scan. Scan will complete in 2 minutes, or sooner if some
// other process initiates a WLAN scan.
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
EBearerIdWLAN,
0,
KWlanNetworks,
wlanPtr,
status );
// To cancel the WLAN scan request:
monitor.CancelAsyncRequest( EConnMonGetPckgAttribute );
User::WaitForRequest( status ); // Should return immediately
error = status.Int();
if ( error == KErrNone ) { /* Request was completed before cancel */ }
else if ( error == KErrCancel ) { /* Request has been cancelled */ }
else { /* Error */ }
delete wlanBuf;
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Stopping a connection
The following example shows how to close a connection using ConnMon API.
// To close a specific connection:
// (requires NetworkServices and NetworkControl capabilities)
TInt error = monitor.SetBoolAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KConnectionStop,
ETrue );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// To close all connections:
// (requires NetworkServices and NetworkControl capabilities)
TInt error = monitor.SetBoolAttribute(
EBearerIdAll,
0,
KConnectionStopAll,
ETrue );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
Registering for events
The following example shows how to register as an event listener for ConnMon
events. Most events are sent to registered listeners by default, but some
events are disabled by default because they are heavier and cause extra processing.
If the client is interested in these special events, the relevant threshold
values need to be set before calling
NotifyEventL()
. See
Section 3.5.1
for a list of these events.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
TUint connectionCount( 0 );
TUint subConnectionCount( 0 );
TUint connectionId( 0 );
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Get connection count
monitor.GetConnectionCount(
connectionCount,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
if ( connectionCount == 0 ) { /* No connection */ }
// Get connection info (1st connection)
TInt error = monitor.GetConnectionInfo(
1,
connectionId,
subConnectionCount );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Some events are not sent by default. To receive them, relevant threshold
// values need to be set before registering the event listener.
// To receive EConnMonConnectionActivityChange events for a specific connection
error = monitor.SetUintAttribute( connectionId, 0, KActivityTimeThreshold, 10 );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// To receive EConnMonDownlinkDataThreshold events for a specific connection
error = monitor.SetUintAttribute( connectionId, 0, KDownlinkDataThreshold, 32768 );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// To receive EConnMonUplinkDataThreshold events for a specific connection
error = monitor.SetUintAttribute( connectionId, 0, KUplinkDataThreshold, 16384 );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// To receive EConnMonBearerAvailabilityChange events
error = monitor.SetUintAttribute( EBearerIdAll, 0, KBearerAvailabilityThreshold, 1 );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// To receive EConnMonSignalStrengthChange events
error = monitor.SetUintAttribute( EBearerIdAll, 0, KSignalStrengthThreshold, 1 );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// To receive EConnMonBearerInfoChange and EConnMonBearerGroupChange events
// instead of the more limited EConnMonBearerChange event
error = monitor.SetUintAttribute( EBearerIdAll, 0, KBearerGroupThreshold, 1 );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Register for events. iObserver is an instance of the class that implements
// the event handler. In this example it’s an instance of MyClass (See next
// use case)
CMyConnMonObserver* iObserver = new( ELeave ) CMyConnMonObserver();
error = monitor.NotifyEventL( *iObserver );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// ...
// Events must be cancelled and RConnectionMonitor object closed when not
// needed any more.
monitor.CancelNotifications();
delete iObserver;
iObserver = NULL;
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Events that are disabled by default
The following events are disabled by default. For a client to receive these
events, the corresponding threshold variable needs to be set.
-
Enabled
with TUint attribute
.
-
Enabled
with TUint attribute
.
-
Enabled
with TUint attribute
.
-
Enabled
with TUint attribute
.
-
Enabled
with TUint attribute
.
-
Enabled
with TUint attribute
.
Will also enable
events
and disable
events.
-
Enabled
with TUint attribute
.
Will also enable
events
and disable
events.
Related APIs
Catching events
The following example shows an example implementation of a ConnMon event
handler. Normally a client is only interested in a limited set of ConnMon
events and ignores the rest.
class CMyConnMonObserver : public CBase, public MConnectionMonitorObserver
{
private:
void EventL( const CConnMonEventBase& aEvent );
};
void CMyConnMonObserver::EventL( const CConnMonEventBase& aEvent )
{
switch( aEvent.EventType() )
{
case EConnMonCreateConnection:
{
CConnMonCreateConnection* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonCreateConnection* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
}
break;
case EConnMonDeleteConnection:
{
CConnMonDeleteConnection* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonDeleteConnection* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
TUint downlinkData = realEvent->DownlinkData();
TUint uplinkData = realEvent->UplinkData();
TBool authoritativeDelete = realEvent->AuthoritativeDelete();
}
break;
case EConnMonCreateSubConnection:
{
CConnMonCreateSubConnection* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonCreateSubConnection* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
TUint subConnectionId = realEvent->SubConnectionId();
}
break;
case EConnMonDeleteSubConnection:
{
CConnMonDeleteSubConnection* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonDeleteSubConnection* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
TUint subConnectionId = realEvent->SubConnectionId();
TUint downlinkData = realEvent->DownlinkData();
TUint uplinkData = realEvent->UplinkData();
TBool authoritativeDelete = realEvent->AuthoritativeDelete();
}
break;
case EConnMonDownlinkDataThreshold:
{
CConnMonDownlinkDataThreshold* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonDownlinkDataThreshold* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
TUint subConnectionId = realEvent->SubConnectionId();
TUint downlinkData = realEvent->DownlinkData();
}
break;
case EConnMonUplinkDataThreshold:
{
CConnMonUplinkDataThreshold* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonUplinkDataThreshold* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
TUint subConnectionId = realEvent->SubConnectionId();
TUint uplinkData = realEvent->UplinkData();
}
break;
case EConnMonNetworkStatusChange:
{
CConnMonNetworkStatusChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonNetworkStatusChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
// TConnMonNetworkStatus
TInt networkStatus = realEvent->NetworkStatus();
}
break;
case EConnMonConnectionStatusChange:
{
CConnMonConnectionStatusChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonConnectionStatusChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
TUint subConnectionId = realEvent->SubConnectionId();
TInt connectionStatus = realEvent->ConnectionStatus();
// See nifvar.h for details on connection status values
}
break;
case EConnMonConnectionActivityChange:
{
CConnMonConnectionActivityChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonConnectionActivityChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
TUint subConnectionId = realEvent->SubConnectionId();
TBool connectionActivity = realEvent->ConnectionActivity();
}
break;
case EConnMonNetworkRegistrationChange:
{
CConnMonNetworkRegistrationChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonNetworkRegistrationChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
// TConnMonNetworkRegistration
TInt networkRegistrationStatus = realEvent->RegistrationStatus();
}
break;
case EConnMonBearerChange:
{
CConnMonBearerChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonBearerChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
TInt bearerChange = realEvent->Bearer();
}
break;
case EConnMonSignalStrengthChange:
{
CConnMonSignalStrengthChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonSignalStrengthChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
TInt signalStrengthChange = realEvent->SignalStrength();
}
break;
case EConnMonBearerAvailabilityChange:
{
CConnMonBearerAvailabilityChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonBearerAvailabilityChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
TBool bearerAvailability = realEvent->Availability();
}
break;
case EConnMonIapAvailabilityChange:
{
CConnMonIapAvailabilityChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonIapAvailabilityChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
TConnMonIapInfo iaps = realEvent->IapAvailability();
for ( TUint i = 0; i < iaps.Count(); i++ )
{
TUint iapId = iaps.iIap[i].iIapId;
}
}
break;
case EConnMonTransmitPowerChange:
{
CConnMonTransmitPowerChange* realEvent;
realEvent = (CConnMonTransmitPowerChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
TUint txPwrNow = realEvent->TransmitPower();
}
break;
case EConnMonSNAPsAvailabilityChange:
{
CConnMonSNAPsAvailabilityChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonSNAPsAvailabilityChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
TUint snapCount = realEvent->SNAPsAvailabile();
TConnMonSNAPInfo snaps = realEvent->SNAPAvailability();
for ( TUint i = 0; i < snaps.Count(); i++ )
{
TUint snapId = snaps.iSNAP[i].iSNAPId;
}
}
break;
case EConnMonNewWLANNetworkDetected:
{
CConnMonNewWLANNetworkDetected* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonNewWLANNetworkDetected* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
}
break;
case EConnMonOldWLANNetworkLost:
{
CConnMonOldWLANNetworkLost* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonOldWLANNetworkLost* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
}
break;
case EConnMonPacketDataAvailable:
{
CConnMonPacketDataAvailable* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonPacketDataAvailable* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
}
break;
case EConnMonPacketDataUnavailable:
{
CConnMonPacketDataUnavailable* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonPacketDataUnavailable* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId(); // generic
}
break;
case EConnMonBearerInfoChange:
{
CConnMonBearerInfoChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonBearerInfoChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
TInt bearerInfo = realEvent->BearerInfo(); // TConnMonBearerInfo
}
break;
case EConnMonBearerGroupChange:
{
CConnMonBearerGroupChange* realEvent;
realEvent = ( CConnMonBearerGroupChange* ) &aEvent;
TUint connectionId = realEvent->ConnectionId();
TBool bearerGroupInternal = realEvent->Internal();
TUint bearerGroups1 = 0;
TUint bearerGroups2 = 0;
// TConnMonBearerGroup
realEvent->BearerGroups( bearerGroups1, bearerGroups2 );
}
break;
default:
// For future events, unrecognized events must not crash the application
break;
}
}
EConnMonCreateConnection event
This event is triggered when a new connection has been created. The connection
ID passed in the event is a new ID number ConnMon assigned to the new connection.
EConnMonDeleteConnection event
This event is triggered when a connection has been deleted. The connection
ID passed in the event is the connection ID of the deleted connection.
EConnMonCreateSubConnection event
This event is triggered when a new subconnection has been created. Subconnections
are not supported currently.
EConnMonDeleteSubConnection event
This event is triggered when a subconnection has been deleted. Subconnections
are not supported currently.
EConnMonDownlinkDataThreshold event
This event is triggered when there is a sufficient change in the volume
of downlink data for a specific connection. The event is sent each time a
client specified amount (
KDownlinkDataThreshold
) of new data
has been sent. If another ConnMon client has requested for these events for
the same connection, the smallest threshold value is used globally. If
KDownlinkDataThreshold
is
0 (default), events are not sent for that connection. To prevent rapid flooding
of these events, different bearers have appropriate minimum threshold values
which is used to override too small thresholds when necessary.
See TUint attributes
and
.
Related APIs
EConnMonUplinkDataThreshold event
This event is triggered when there is a sufficient change in the volume
of uplink data for a specific connection. The event is sent each time a client
specified amount (
KUplinkDataThreshold
) of new data has been
received. If another ConnMon client has requested for these events for the
same connection, the smallest threshold value will be used globally. If
KUplinkDataThreshold
is
0 (default), events are not sent for that connection. To prevent rapid flooding
of these events, different bearers have appropriate minimum threshold values
which are used to override too small thresholds when necessary.
See TUint attributes
and
.
Related APIs
EConnMonNetworkStatusChange event
This event is triggered when network status changes for some packet data
connection. The connection ID passed in the event is a bearer specific connection
ID (see
TConnMonBearerId
). The same information can be retrieved
with TInt attribute
KNetworkStatus
.
See TInt attribute
.
Related APIs
-
KNetworkStatus
-
TConnMonBearerId
EConnMonConnectionStatusChange event
This event is triggered when the status of some connection changes. The
same information can be retrieved with TInt attribute
KConnectionStatus
.
Connection status values are defined in
nifvar.h
.
See TInt attribute
.
Related APIs
EConnMonConnectionActivityChange event
This event is triggered when some connection changes from active to idle
or vice versa. The client must set
KActivityTimeThreshold
to
receive these events.
KActivityTimeThreshold
defines the
period (in seconds) for checking whether the connection is active or not.
The minimum allowed value is 5 seconds. The connection is considered active,
if data has been passed during the last period, otherwise it is considered
inactive. The same information can be retrieved with TBool attribute
KConnectionActive
.
See TUint attribute
and
TBool attribute
.
Related APIs
-
KActivityTimeThreshold
-
KConnectionActive
EConnMonNetworkRegistrationChange event
This event is triggered when network registration status (GSM/GPRS/WCDMA)
changes. The connection ID passed in the event is a bearer specific connection
ID (see
TConnMonBearerId
). The same information can be retrieved
with TInt attribute
KNetworkRegistration
. Network registration
values are defined in
TConnMonNetworkRegistration
.
See TInt attribute
.
Related APIs
-
KNetworkRegistration
-
TConnMonBearerId
-
TConnMonNetworkRegistration
EConnMonBearerChange event
This event is triggered when bearer type (GPRS/EdgeGPRS/WCDMA) changes.
The connection ID passed in the event is a bearer specific connection ID,
either
EBearerIdGPRS
or
EBearerIdWCDMA
(see
TConnMonBearerId
).
The new bearer passed in the event can be
EBearerGPRS
,
EBearerEdgeGPRS
or
EBearerWCDMA
(see
TConnMonBearerType
). The same information can be retrieved with
TInt attribute
KBearer
.
Note: If TUint attribute
KBearerGroupThreshold
is set,
these events are disabled and events
EConnMonBearerInfoChange
and
EConnMonBearerGroupChange
are
used instead. Use these events, for example, if HSDPA related information
is required.
See TInt attribute
and
TUint attribute
.
Related APIs
-
EBearerEdgeGPRS
-
EBearerGPRS
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EBearerWCDMA
-
EConnMonBearerGroupChange
-
EConnMonBearerInfoChange
-
KBearer
-
KBearerGroupThreshold
-
TConnMonBearerId
-
TConnMonBearerType
EConnMonSignalStrengthChange event
This event is triggered when signal strength changes. The connection ID
passed in the event is a bearer specific connection ID (see
TConnMonBearerId
).
This event is valid only for cellular (GPRS, WCDMA, etc.) bearers and not
for other bearers, e.g. WLAN. The client must set
KSignalStrengthThreshold
to
1 to receive these events.
See TInt attribute
and
TUint attribute
.
Related APIs
-
KSignalStrengthThreshold
-
TConnMonBearerId
EConnMonBearerAvailabilityChange event
This event is triggered when the availability of some bearer changes. The
connection ID passed in the event is a bearer specific connection ID (see
TConnMonBearerId
).
The client must set
KBearerAvailabilityThreshold
to 1 to
receive these events. Using this event for detecting changes in WLAN availability
requires WLAN background scanning to be enabled.
See TUint attribute
and
TBool attribute
.
Related APIs
-
KBearerAvailabilityThreshold
-
TConnMonBearerId
EConnMonIapAvailabilityChange event
This event is triggered when IAP availability changes. The connection ID
passed in the event is the generic connection ID
EBearerIdAll
.
The ID numbers of available IAPs are included in the event (see
TConnMonIapInfo
).
The same information can be retrieved with packaged attribute
KIapAvailability
.
See packaged attribute
.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdAll
-
KIapAvailability
-
TConnMonIapInfo
EConnMonTransmitPowerChange event
This event is triggered when the used WLAN transmit power changes. The
connection ID passed in the event is the bearer specific connection ID
EBearerIdWLAN
.
Transmit power is given in milliwatts (mW). The same information can be retrieved
with TUint attribute
KTransmitPower
.
See TUint attribute
.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
KTransmitPower
EConnMonSNAPsAvailabilityChange event
This event is triggered when SNAP availability changes. The connection
ID passed in the event is the generic connection ID
EBearerIdAll
.
The ID numbers of available SNAPs are included in the event (see
TConnMonSNAPInfo
).
The same information can be retrieved with packaged attributes
KSNAPsAvailability
and
KAvailableSNAPsIds
.
See packaged attributes
and
.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdAll
-
KAvailableSNAPsIds
-
KSNAPsAvailability
-
TConnMonSNAPInfo
EConnMonNewWLANNetworkDetected event
This event is triggered when new WLAN networks are detected during a WLAN
scan. The connection ID passed in the event is the bearer specific connection
ID
EBearerIdWLAN
. To receive these events, WLAN background
scanning must be enabled, or some other mechanism must be used to trigger
the necessary WLAN scans.
Related APIs
EConnMonOldWLANNetworkLost event
This event is triggered when one or more WLAN networks have been lost since
the last WLAN scan. The connection ID passed in the event is the bearer specific
connection ID
EBearerIdWLAN
. To receive these events, WLAN
background scanning must be enabled, or some other mechanism must be used
to trigger the necessary WLAN scans.
Related APIs
EConnMonPacketDataAvailable event
This event is triggered when GPRS or WCDMA bearer availability changes,
a phone call is started, or a phone call ends. The connection ID passed in
the event is a bearer specific connection ID, either
EBearerIdGPRS
or
EBearerIdWCDMA
(see
TConnMonBearerId
).
EConnMonPacketDataAvailable
and
EConnMonPacketDataUnavailable
events
form a pair. Two events are always sent, one with connection ID
EBearerIdGPRS
for
2G network, and one with connection ID
EBearerIdWCDMA
for
3G network. The event for the network that the phone is not registered to
is always of type
EConnMonPacketDataUnavailable
. If the phone
does not support dual transfer mode and a call is started, a GPRS or WCDMA
packet data connection is put on hold. In this scenario, both are of type
EConnMonPacketDataUnavailable
.
The same information can be retrieved with TBool attribute
KPacketDataAvailability
.
See TBool attribute
.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EConnMonPacketDataAvailable
-
EConnMonPacketDataUnavailable
-
KPacketDataAvailability
-
TConnMonBearerId
EConnMonPacketDataUnavailable event
This event is triggered when GPRS or WCDMA bearer availability changes,
a phone call is started, or a phone call ends. The connection ID passed in
the event is a bearer specific connection ID, either
EBearerIdGPRS
or
EBearerIdWCDMA
(see
TConnMonBearerId
).
EConnMonPacketDataUnavailable
and
EConnMonPacketDataAvailable
events
form a pair. Two events are always sent, one with connection ID
EBearerIdGPRS
for
2G network, and one with connection ID
EBearerIdWCDMA
for
3G network. The event for the network that the phone is not registered to
is always of type
EConnMonPacketDataUnavailable
. If the phone
does not support dual transfer mode and a call is started, a GPRS or WCDMA
packet data connection is put on hold. In this scenario, both are of type
EConnMonPacketDataUnavailable
.
The same information can be retrieved with TBool attribute
KPacketDataAvailability
.
See TBool attribute
.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EConnMonPacketDataAvailable
-
EConnMonPacketDataUnavailable
-
KPacketDataAvailability
-
TConnMonBearerId
EConnMonBearerInfoChange
This event is triggered when there is a change in bearer information for
an existing connection, or if the network mode changes e.g. from 2G to 3G.
For connection specific events, the connection ID passed in the event is the
respective connection specific ID, and for network level events, the connection
ID is
EBearerIdAll
. The same connection level information
can be retrieved with TInt attribute
KBearerInfo
. The bearer
info values are defined in
TConnMonBearerInfo
.
Note: The client needs to set the TUint attribute
KBearerGroupThreshold
in
order to receive these events. This also disables the
EConnMonBearerChange
events.
See TInt attribute
,
TUint attribute
and
event.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdAll
-
EConnMonBearerChange
-
KBearerGroupThreshold
-
KBearerInfo
-
TConnMonBearerInfo
EConnMonBearerGroupChange event
This event is triggered when there is a change in bearer group information
for an existing connection. The connection ID passed in the event is the respective
connection specific ID. The same information can be retrieved with packaged
attribute
KBearerGroupInfo
. The bearer group bitmask is defined
in
TConnMonBearerGroup
.
Note: The client needs to set the TUint attribute
KBearerGroupThreshold
in
order to receive these events. This also disables
EConnMonBearerChange
events.
See packaged attribute
,
TUint attribute
and
event.
Related APIs
-
EConnMonBearerChange
-
KBearerGroupInfo
-
KBearerGroupThreshold
-
TConnMonBearerGroup
Using TInt attributes
These attributes are used with
RConnectionMonitor::GetIntAttribute()
and
RConnectionMonitor::SetIntAttribute()
methods.
KBearer attribute
Used with
GetIntAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection, or the bearer specific
connection ID
EBearerIdGPRS
.
This attribute is used to retrieve the bearer of a connection. If the bearer
specific connection ID
EBearerIdGPRS
is used as connection
ID parameter, ConnMon checks if EDGE is in use. If yes,
EBearerEdgeGPRS
is
returned, if not,
EBearerGPRS
is returned. Connection bearer
types are defined in
TConnMonBearerType
.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EBearerEdgeGPRS
-
EBearerGPRS
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
GetIntAttribute()
-
TConnMonBearerType
-
aConnectionId
KNetworkStatus attribute
Used with
GetIntAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection, or a bearer specific
connection ID. Supported bearer specific connection IDs are:
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
This attribute is used to retrieve the current network status of the phone.
Network status values are defined in
TConnMonNetworkStatus
.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
GetIntAttribute()
-
TConnMonNetworkStatus
-
aConnectionId
KConnectionStatus attribute
Used with
GetIntAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the current status/progress information
of a connection. Connection status values are defined in
nifvar.h
.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
GetIntAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KProtocolType attribute
Used with
GetIntAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the protocol type (type of PDP) of a
connection. Protocol types are defined in
TConnMonProtocolType
.
Related APIs
-
GetIntAttribute()
-
TConnMonProtocolType
-
aConnectionId
KNetworkRegistration attribute
Used with
GetIntAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection, or a bearer specific
connection ID. Supported bearer specific connection IDs are:
-
EBearerIdCSD
-
EBearerIdGSM
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EBearerIdWcdmaCSD
This attribute is used to retrieve the current network registration status
of the phone. Network registration values are defined in
TConnMonNetworkRegistration
.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdCSD
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdGSM
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EBearerIdWcdmaCSD
-
GetIntAttribute()
-
TConnMonNetworkRegistration
-
aConnectionId
KSignalStrength attribute
Used with
GetIntAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection, or a bearer specific
connection ID. Supported bearer specific connection IDs are:
-
EBearerIdCSD
-
EBearerIdGSM
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EBearerIdWcdmaCSD
-
EBearerIdWLAN
This attribute is used to retrieve the current signal strength. For WLAN,
if an active WLAN connection is present, the signal strength of that connection
is returned. Otherwise a WLAN scan is performed and the signal strength of
the strongest network found is returned.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdCSD
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdGSM
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
EBearerIdWcdmaCSD
-
GetIntAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KNetworkMode attribute
Used with
GetIntAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing WLAN connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the network mode of an active WLAN connection.
WLAN network modes are defined in
TConnMonNetworkMode
.
Related APIs
-
GetIntAttribute()
-
TConnMonNetworkMode
-
aConnectionId
KSecurityMode attribute
Used with
GetIntAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing WLAN connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the security mode of an active WLAN
connection. WLAN connection security modes are defined in
TConnMonSecurityMode
.
Related APIs
-
GetIntAttribute()
-
TConnMonSecurityMode
-
aConnectionId
KBearerInfo attribute
Used with
GetIntAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the current bearer information for an
existing connection. Bearer information values are defined in
TConnMonBearerInfo
.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
GetIntAttribute()
-
TConnMonBearerInfo
-
aConnectionId
KWlanScanCacheLifetime attribute
Used with
GetIntAttribute()
and
SetIntAttribute()
.
Parameter
aConnectionId
must be a valid connection ID for
an existing WLAN connection, or the bearer specific connection ID
EBearerIdWLAN
.
This attribute is used to control the behaviour of WLAN scanning together
with TUint attribute
KWlanScanMaxDelay
. These attributes
are client specific, and do not directly affect other ConnMon clients.
KWlanScanCacheLifetime
represents
the age (in seconds) of WLAN scan results that the client is willing to accept.
The valid value range is 0-60 seconds. Greater values are automatically set
to the maximum allowed value. The value -1 represents the device specific
default value (usually 7 seconds). The bigger this value is, the more likely
it is there will be a suitable WLAN scan result in cache when a WLAN scan
request is made. This leads to faster completion of WLAN scan requests and
also less frequent WLAN scanning performed by the device, which in turn leads
to longer battery life.
Note:
KWlanScanCacheLifetime
attribute is ignored unless
TUint attribute
KWlanScanMaxDelay
is set to 0.
See TUint attribute
.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
GetIntAttribute()
-
KWlanScanCacheLifetime
-
KWlanScanMaxDelay
-
SetIntAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
Related APIs
-
RConnectionMonitor::GetIntAttribute()
-
RConnectionMonitor::SetIntAttribute()
Using TUint attributes
These attributes are used with the
RConnectionMonitor::GetUintAttribute()
and
RConnectionMonitor::SetUintAttribute()
methods.
KDownlinkData attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the amount of data in bytes transferred
by this connection from the remote endpoint.
Related APIs
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KUplinkData attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the amount of data in bytes transferred
by this connection to the remote endpoint.
Related APIs
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KIAPId attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the IAP ID of an active connection.
Related APIs
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KNetworkIdentifier attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the network ID of an active connection.
Related APIs
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KTransmitPower attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing WLAN connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the transmit power of an active WLAN
connection.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KMobilePhoneNetworkMode attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
is
not used with this attribute.
This attribute is used to retrieve the current phone network mode. The
network modes are defined in
TConnMonMobilePhoneNetworkMode
.
See the
and
events.
Related APIs
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
TConnMonMobilePhoneNetworkMode
-
aConnectionId
KActivityTimeThreshold attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
and
SetUintAttribute()
.
Parameter
aConnectionId
must be a valid connection ID for
an existing connection.
This attribute controls connection activity monitoring for a connection.
It defines the period (in seconds) for checking whether the connection is
active or not. The minimum allowed value is 5 seconds. The default value 0
means monitoring is disabled and
EConnMonConnectionActivityChange
events
are not sent for this connection. If set to a value in between these, the
minimum allowed value is used.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EConnMonConnectionActivityChange
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
SetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KDownlinkDataThreshold attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
and
SetUintAttribute()
.
Parameter
aConnectionId
must be a valid connection ID for
an existing connection.
This attribute controls downlink data amount monitoring for a connection.
It defines the amount of data (in bytes) that needs to be received by a connection
before a new
EConnMonDownlinkDataThreshold
event is generated.
The minimum allowed value is 4096 bytes, but this can be higher depending
on the bearer of the connection. This is to prevent event flooding on higher
bandwidth networks. The default value 0 means monitoring is disabled and the
EConnMonDownlinkDataThreshold
events
are not sent for this connection.
The bearer specific minimum values are:
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EConnMonDownlinkDataThreshold
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
SetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KUplinkDataThreshold attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
and
SetUintAttribute()
.
Parameter
aConnectionId
must be a valid connection ID for
an existing connection.
This attribute controls uplink data amount monitoring for a connection.
It defines the amount of data (in bytes) that needs to be sent by a connection
before a new
EConnMonUplinkDataThreshold
event is generated.
The minimum allowed value is 4096 bytes, but this can be higher depending
on the bearer of the connection. This is to prevent event flooding on higher
bandwidth networks. The default value 0 means monitoring is disabled and the
EConnMonUplinkDataThreshold
events
are not sent for this connection.
The bearer specific minimum values are:
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EConnMonUplinkDataThreshold
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
SetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KBearerAvailabilityThreshold attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
and
SetUintAttribute()
.
Parameter
aConnectionId
is not used with this attribute.
This attribute controls bearer availability monitoring. Set to 1 to receive
notifications from ConnMon when bearer availability changes. The default value
0 means monitoring is disabled and the
EConnMonBearerAvailabilityChange
events
are not sent.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EConnMonBearerAvailabilityChange
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
SetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KSignalStrengthThreshold attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
and
SetUintAttribute()
.
Parameter
aConnectionId
is not used with this attribute.
This attribute controls cellular network signal strength monitoring. Set
to 1 to receive notifications from ConnMon when cellular network signal strength
changes. The default value 0 means monitoring is disabled and the
EConnMonSignalStrengthChange
events
are not sent.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EConnMonSignalStrengthChange
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
SetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KBearerGroupThreshold attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
and
SetUintAttribute()
.
Parameter
aConnectionId
is not used with this attribute.
This attribute controls whether ConnMon is sending a client
EConnMonBearerChange
events,
or
EConnMonBearerInfoChange
and
EConnMonBearerGroupChange
events.
The new
EConnMonBearerChange
and
EConnMonBearerInfoChange
events
are more up to date, and designed to be extendable. Set to 1 to take them
into use. The default value 0 means
EConnMonBearerChange
events
are used instead, and
EConnMonBearerInfoChange
and
EConnMonBearerGroupChange
are
not sent.
See the
,
and
events.
Related APIs
-
EConnMonBearerChange
-
EConnMonBearerGroupChange
-
EConnMonBearerInfoChange
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
SetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KWlanScanMaxDelay attribute
Used with
GetUintAttribute()
and
SetUintAttribute()
.
Parameter
aConnectionId
must be a valid connection ID for
an existing WLAN connection, or the bearer specific connection ID
EBearerIdWLAN
.
This attribute is used to control the behaviour of WLAN scanning together
with TInt attribute
KWlanScanCacheLifetime
. These attributes
are client specific, and do not directly affect other ConnMon clients.
KWlanScanMaxDelay
represents
the time (in seconds) the client is willing to wait for WLAN scan results.
These WLAN scan results will be up to date, and thus the device is forced
to perform a WLAN scan. The valid value range is 0-1200 seconds. Greater values
are automatically set to the maximum allowed value. If another process triggers
a WLAN scan while a scan request is waiting for this delay, the request is
completed early with the fresh scan results.
Note: When
KWlanScanMaxDelay
is set to 0 (the default
value), cached WLAN scan results may be used instead. TInt attribute
KWlanScanCacheLifetime
can
be used to control the maximum allowed age of these cached WLAN scan results.
See the TInt attribute
.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
GetUintAttribute()
-
KWlanScanCacheLifetime
-
KWlanScanMaxDelay
-
SetUintAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
Related APIs
-
RConnectionMonitor::GetUintAttribute()
-
RConnectionMonitor::SetUintAttribute()
Using TBool attributes
These attributes are used with the
RConnectionMonitor::GetBoolAttribute()
and
RConnectionMonitor::SetBoolAttribute()
methods.
KConnectionActive attribute
Used with
GetBoolAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to check if a connection is active or not. If
EConnMonConnectionActivityChange
events
are enabled for this connection, ConnMon returns the current cached information
immediately. If these events are not enabled (default), ConnMon completes
this request in approximately 1 second. The connection is considered active,
if data has been passed during this time, otherwise it is considered inactive.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EConnMonConnectionActivityChange
-
GetBoolAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KBearerAvailability attribute
Used with
GetBoolAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection, or a bearer specific
connection ID. Supported bearer specific connection IDs are:
-
EBearerIdCSD
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EBearerIdWcdmaCSD
-
EBearerIdWLAN
This attribute is used to find out if a bearer is currently available.
To check for a specific bearer, the given connection ID should be one of the
bearer specific connection IDs. If the given connection ID belongs to a valid
connection, the availability of the bearer used by that connection is checked.
See the
event.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdCSD
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
EBearerIdWcdmaCSD
-
GetBoolAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KPacketDataAvailability attribute
Used with
GetBoolAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a bearer specific connection ID. Supported bearer specific connection IDs
are:
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
This attribute is used to retrieve the packet data availability status
for a 2G or 3G network. The status is false if the bearer is not available,
or the phone does not support dual transfer mode and a phone call is currently
active.
See the
and
events.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
GetBoolAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KConnectionStop attribute
Used with
SetBoolAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
By setting this attribute to
ETrue
, the connection referred
to by the connection ID is closed.
Note: The client must have the
NetworkServices
and
NetworkControl
capabilities
to use this attribute.
Related APIs
-
ETrue
-
NetworkControl
-
NetworkServices
-
SetBoolAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KConnectionStopAll attribute
Used with
SetBoolAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
is
not used with this attribute.
By setting this attribute to
ETrue
, all connections on
the device are closed.
Note: The client must have the
NetworkServices
and
NetworkControl
capabilities
to use this attribute.
Related APIs
-
ETrue
-
NetworkControl
-
NetworkServices
-
SetBoolAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
Related APIs
-
RConnectionMonitor::GetBoolAttribute()
-
RConnectionMonitor::SetBoolAttribute()
Using string attributes
These attributes are used with the
RConnectionMonitor::GetStringAttribute()
and
RConnectionMonitor::SetStringAttribute()
methods.
KIAPName attribute
Used with
GetStringAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the IAP name a connection is connected
through.
Related APIs
-
GetStringAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KAccessPointName attribute
Used with
GetStringAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the access point name from the IAP the
connection is connected through.
Related APIs
-
GetStringAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KTelNumber attribute
Used with
GetStringAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the used telephone number for a connection,
when applicable.
Related APIs
-
GetStringAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KNetworkName attribute
Used with
GetStringAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing WLAN connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the network name (SSID) of the WLAN
that a connection is connected to. A WLAN name can be up to 32 characters
long.
Related APIs
-
GetStringAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KWlanSsid attribute
Used with
GetStringAttribute()
and
SetStringAttribute()
.
Parameter
aConnectionId
must be a valid connection ID for
an existing WLAN connection, or the bearer specific connection ID
EBearerIdWLAN
.
This attribute is used to set the SSID value to be used when performing
a WLAN scan for networks with a specific SSID.
See the packaged attribute
.
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
GetStringAttribute()
-
SetStringAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
Related APIs
-
RConnectionMonitor::GetStringAttribute()
-
RConnectionMonitor::SetStringAttribute()
Using packaged attributes
These attributes are used with the
RConnectionMonitor::GetPckgAttribute()
method.
KStartTime attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve a connections start time. The information
is transferred through a package (see
TConnMonTimeBuf
).
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
TUint connectionCount( 0 );
TUint subConnectionCount( 0 );
TUint connectionId( 0 );
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Get connection count
monitor.GetConnectionCount(
connectionCount,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
if ( connectionCount == 0 ) { /* No connection */ }
// Get connection info (1st connection)
TInt error = monitor.GetConnectionInfo(
1,
connectionId,
subConnectionCount );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get connection duration (1st connection)
TConnMonTimeBuf timeBuffer;
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KStartTime,
timeBuffer,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
TTimeIntervalSeconds connectionDurationInSecs;
TTime now;
now.UniversalTime();
now.SecondsFrom( timeBuffer(), connectionDurationInSecs );
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
TConnMonTimeBuf
-
aConnectionId
KClientInfo attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve the client UID for all clients using
a specific connection. ConnMon does not include itself in the results. The
information is transferred through a package (see
TConnMonClientEnumBuf
).
The package class has a fixed size array and is limited to a maximum of 10
(
KConnMonMaxClientUids
) UIDs.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
TUint connectionCount( 0 );
TUint subConnectionCount( 0 );
TUint connectionId( 0 );
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Get connection count
monitor.GetConnectionCount(
connectionCount,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
if ( connectionCount == 0 ) { /* No connection */ }
// Get connection info (1st connection)
TInt error = monitor.GetConnectionInfo(
1,
connectionId,
subConnectionCount );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */}
// Get connection client info
TConnMonClientEnumBuf buf;
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KClientInfo,
buf,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
TUint clientCount = buf().iCount;
for ( TInt i = 0; i < clientCount; i++ )
{
TInt32 clientUid = buf().iUid[i].iUid;
// ...
}
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
KConnMonMaxClientUids
-
TConnMonClientEnumBuf
-
aConnectionId
KNetworkNames attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing WLAN connection, or the bearer specific
connection ID
EBearerIdWLAN
.
This attribute is used to retrieve information about available WLANs. This
includes the network name (SSID), signal strength and mode (see
TConnMonNetworkMode
).
A WLAN scan is performed to obtain this information. The networks are sorted
according to signal strength, strongest network first. The information is
transferred through a package (see
TConnMonNetworkNamesBuf
).
The package class has a fixed size array and is limited to a maximum of 10
(
KConnMonMaxNetworkCount
) network information objects.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Buffer for basic WLAN information (max. 10 networks)
TConnMonNetworkNamesBuf buf;
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
EBearerIdWLAN,
0,
KNetworkNames,
buf,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
TInt wlanCount = buf().Count();
TBuf<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KMaxNameLength> wlanName;
TInt wlanSignalStrength = 0;
TInt wlanMode = 0; // TConnMonNetworkMode
for ( TInt i = 0; i < wlanCount; i++ )
{
wlanName.Copy( buf().iNetwork[i].iName );
wlanSignalStrength = buf().iNetwork[i].iSignalStrength;
wlanMode = buf().iNetwork[i].iType;
// ...
}
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
KConnMonMaxNetworkCount
-
TConnMonNetworkMode
-
TConnMonNetworkNamesBuf
-
aConnectionId
KIapAvailability attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a bearer specific connection ID. Supported bearer specific connection IDs
are:
-
EBearerIdAll
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EBearerIdCSD
-
EBearerIdWcdmaCSD
-
EBearerIdLAN
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
EBearerIdVirtualVPN
This attribute is used to retrieve bearer specific available IAP IDs, or
all available IAP IDs, depending on the given connection ID. The information
is transferred through a package (see
TConnMonIapInfoBuf
).
The package class has a fixed size array and is limited to a maximum of 25
(
KConnMonMaxIAPCount
) IDs.
See the
event.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Buffer for IAP info
TConnMonIapInfoBuf iapBuffer;
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
EBearerIdAll,
0,
KIapAvailability,
iapBuffer,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
TUint iapCount = iapBuffer().Count();
for ( TInt i = 0; i < iapCount; i++ )
{
TUint iapId = iapBuffer().iIap[i].iIapId;
// ...
}
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
EBearerIdAll
-
EBearerIdCSD
-
EBearerIdGPRS
-
EBearerIdLAN
-
EBearerIdVirtualVPN
-
EBearerIdWCDMA
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
EBearerIdWcdmaCSD
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
KConnMonMaxIAPCount
-
TConnMonIapInfoBuf
-
aConnectionId
KSNAPsAvailability attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
is
not used with this attribute.
This attribute is used to retrieve available SNAP IDs. The information
is transferred through a package (see
TConnMonSNAPInfoBuf
).
The package class has a fixed size array and is limited to a maximum of 25
(
KConnMonMaxSNAPsCount
) IDs.
See the
event.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Buffer for SNAP information
TConnMonSNAPInfoBuf snapBuffer;
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
EBearerIdAll,
0,
KSNAPsAvailability,
snapBuffer,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
TUint snapCount = snapBuffer().Count();
for ( TInt i = 0; i < snapCount; i++ )
{
TUint snapId = snapBuffer().iSNAP[i].iSNAPId;
// ...
}
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
KConnMonMaxSNAPsCount
-
TConnMonSNAPInfoBuf
-
aConnectionId
KAvailableSNAPsIds attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
is
not used with this attribute.
This attribute is used to retrieve available SNAP IDs. The information
is transferred through a package (see
ConnMonIdsArrayPckg
).
The package class has a buffer that the client needs to allocate memory for,
thus the size is not limited. The buffer also contains the total amount of
available SNAPs and how many of those fit inside the buffer.
See the
event.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Buffer for SNAP information
ConnMonIdsArrayPckg idBuffer( 32 ); // Buffer size 32
TPtr idBufferPtr( idBuffer.Buf()->Des() );
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
EBearerIdAll,
0,
KAvailableSNAPsIds,
idBufferPtr,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Amount of available SNAP IDs on the phone
TUint totalAmount = idBuffer.Buf()->Des()[0];
// Amount of available SNAP IDs that fit inside the buffer
TUint bufferAmount = idBuffer.Buf()->Des()[1];
if ( bufferAmount != totalAmount )
{
// Buffer was too small, all IDs did not fit.
// Minimum space needed is ( totalAmount * 2 ) + 2
}
// Unpack buffer to an RArray<TConnMonId>
RConnMonIdsArray idArray;
idBuffer.UnpackToL( idArray );
for ( TInt i = 0; i < idArray.Count(); i++ )
{
TConnMonId id = idArray[i];
TUint idNumber = id.Id();
// ...
}
idArray.Close();
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
ConnMonIdsArrayPckg
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
KWlanNetworks attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing WLAN connection, or the bearer specific
connection ID
EBearerIdWLAN
.
This attribute is used to perform a broadcast WLAN scan. The information
is transferred through a package (see
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg
).
The package class has a buffer that the client needs to allocate memory for.
The buffer is filled with WLANs sorted by signal strength, strongest network
first. The buffer also contains the total amount of available WLANs and how
many of those fit inside the buffer.
Note: TInt attribute
KWlanScanCacheLifetime
and TUint
attribute
KWlanScanMaxDelay
can be used to control the timing
and age of the actual scan results.
See the
and
events,
TInt attribute
and
TUint attribute
.
Example how to perform a normal WLAN scan:
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Buffer for WLAN information
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg* wlanBuf =
new( ELeave ) CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg( 2048 );
TPtr wlanPtr( wlanBuf->Buf()->Des() );
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
EBearerIdWLAN,
0,
KWlanNetworks,
wlanPtr,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
RConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArray wlanPtrArray;
wlanBuf->UnpackToL( wlanPtrArray );
// Amount of WLANs found
TUint totalAmount = wlanBuf->Buf()->Des()[0];
// Amount of WLANs that fit inside the buffer
TUint bufferAmount = wlanBuf->Buf()->Des()[1];
for ( TInt i = 0; i < wlanPtrArray.Count(); i++ )
{
TBuf<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KMaxNameLength> wlanName = wlanPtrArray[i]->Name();
TBuf8<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KWlanBssId> wlanBssid = wlanPtrArray[i]->WlanBssid();
TUint wlanConnectionMode = wlanPtrArray[i]->ConnectionMode();
TUint wlanSignalStrength = wlanPtrArray[i]->SignalStrength();
TUint wlanSecurityMode = wlanPtrArray[i]->SecurityMode();
// ...
delete wlanPtrArray[i];
}
wlanPtrArray.Close();
delete wlanBuf;
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Example how to perform a WLAN scan with some voluntary delay added:
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Buffer for WLAN information
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg* wlanBuf =
new( ELeave ) CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg( 2048 );
TPtr wlanPtr( wlanBuf->Buf()->Des() );
// Set a 120 second WLAN scan delay
TUint scanDelay = 120;
TInt error = monitor.SetUintAttribute(
EBearerIdWLAN,
0,
KWlanScanMaxDelay,
scanDelay );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Request a WLAN scan. Scan will complete in 2 minutes, or sooner if some
// other process initiates a WLAN scan.
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
EBearerIdWLAN,
0,
KWlanNetworks,
wlanPtr,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status ); // Will take up to 2 minutes
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
RConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArray wlanPtrArray;
wlanBuf->UnpackToL( wlanPtrArray );
// Amount of WLANs found
TUint totalAmount = wlanBuf->Buf()->Des()[0];
// Amount of WLANs that fit inside the buffer
TUint bufferAmount = wlanBuf->Buf()->Des()[1];
for ( TInt i = 0; i < wlanPtrArray.Count(); i++ )
{
TBuf<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KMaxNameLength> wlanName = wlanPtrArray[i]->Name();
TBuf8<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KWlanBssId> wlanBssid = wlanPtrArray[i]->WlanBssid();
TUint wlanConnectionMode = wlanPtrArray[i]->ConnectionMode();
TUint wlanSignalStrength = wlanPtrArray[i]->SignalStrength();
TUint wlanSecurityMode = wlanPtrArray[i]->SecurityMode();
// ...
delete wlanPtrArray[i];
}
wlanPtrArray.Close();
delete wlanBuf;
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
KWlanScanCacheLifetime
-
KWlanScanMaxDelay
-
aConnectionId
KBearerGroupInfo attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing connection.
This attribute is used to retrieve bearer group information for a connection.
The bearer group information is a bitmask containing bearer type related information.
The bitmask is defined in
TConnMonBearerGroup
. The information
is transferred through a package (see
TConnMonBearerGroupInfoBuf
).
See the
event.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
TUint connectionCount( 0 );
TUint subConnectionCount( 0 );
TUint connectionId( 0 );
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Get connection count
monitor.GetConnectionCount(
connectionCount,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
if ( connectionCount == 0 ) { /* No connection */ }
// Get connection info (1st connection)
TInt error = monitor.GetConnectionInfo(
1,
connectionId,
subConnectionCount );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Get bearer group info
TConnMonBearerGroupInfoBuf bearerGroupInfoBuf;
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KBearerGroupInfo,
bearerGroupInfoBuf,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
TBool internal = bearerGroupInfoBuf().iInternal;
TUint bearerGroupMask = bearerGroupInfoBuf().iBearerGroups;
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
TConnMonBearerGroup
-
TConnMonBearerGroupInfoBuf
-
aConnectionId
KWlanSsidNetworks attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing WLAN connection, or the bearer specific
connection ID
EBearerIdWLAN
.
This attribute is used to perform a WLAN scan for networks with a specific
SSID. The SSID is set with the string attribute
KWlanSsid
.
If the SSID is empty (default), a normal broadcast scan is made. The request
works the same way as package attribute
KWlanNetworks
, but
multiple simultaneous SSID scan requests from one client are not allowed.
Any extra concurrent requests are completed with error code
KErrInUse
.
The information is transferred through a package (see
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg
).
The package class has a buffer that the client needs to allocate memory for.
The buffer is filled with WLANs sorted by signal strength, strongest network
first. The buffer also contains the total amount of available WLANs and how
many of those fit inside the buffer.
See string attribute
and
packaged attribute
.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Buffer for WLAN information
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg* wlanBuf =
new( ELeave ) CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg( 1024 );
TPtr wlanPtr( wlanBuf->Buf()->Des() );
// String attribute for SSID scan
TBuf<32> ssidString;
ssidString.Copy( _L("MyWlan") );
TInt error = monitor.SetStringAttribute(
EBearerIdWLAN,
0,
KWlanSsid,
ssidString );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* error */ }
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
EBearerIdWLAN,
0,
KWlanSsidNetworks,
wlanPtr,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
RConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArray wlanPtrArray;
wlanBuf->UnpackToL( wlanPtrArray );
// Amount of WLANs found
TUint totalAmount = wlanBuf->Buf()->Des()[0];
// Amount of WLANs that fit inside the buffer
TUint bufferAmount = wlanBuf->Buf()->Des()[1];
for ( TInt i = 0; i < wlanPtrArray.Count(); i++ )
{
TBuf<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KMaxNameLength> wlanName = wlanPtrArray[i]->Name();
TBuf8<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KWlanBssId> wlanBssid = wlanPtrArray[i]->WlanBssid();
TUint wlanConnectionMode = wlanPtrArray[i]->ConnectionMode();
TUint wlanSignalStrength = wlanPtrArray[i]->SignalStrength();
TUint wlanSecurityMode = wlanPtrArray[i]->SecurityMode();
// ...
delete wlanPtrArray[i];
}
wlanPtrArray.Close();
delete wlanBuf;
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
KErrInUse
-
KWlanNetworks
-
KWlanSsid
-
aConnectionId
KWlanCurrentNetwork attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing WLAN connection, or the bearer specific
connection ID
EBearerIdWLAN
.
This attribute is used to retrieve information about the currently used
WLAN. The request works the same way as package attribute
KWlanNetworks
.
The information is transferred through a package (see
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg
).
The package class has a buffer that the client needs to allocate memory for,
but it only needs enough memory to contain one WLAN object. If the connection
ID given as parameter is for an existing connection, the request succeeds
only if that connection is using WLAN bearer. In case the connection ID is
invalid or the connection bearer is not WLAN, the request is completed with
KErrArgument
.
If the connection ID given as parameter is
EBearerIdWLAN
,
the request succeeds if there is a WLAN connection active. If not, the request
is completed with
KErrNotFound
.
See packaged attribute
.
Retrieving information about currently used WLAN using the bearer specific
connection ID:
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Buffer for WLAN information
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg* currentWlanBuf =
new( ELeave ) CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg( 80 );
TPtr currentWlanPtr( currentWlanBuf->Buf()->Des() );
// Get info for currently used WLAN
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
EBearerIdWLAN,
0,
KWlanCurrentNetwork,
currentWlanPtr,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() == KErrNotFound ) { /* No WLAN connection active */ }
else if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
else
{
// Process the results
RConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArray currentWlan;
currentWlanBuf->UnpackToL( currentWlan );
// With KWlanCurrentNetwork and no errors, both should be 1
TUint totalAmount = currentWlanBuf->Buf()->Des()[0];
TUint bufferAmount = currentWlanBuf->Buf()->Des()[1];
for ( TInt i = 0; i < currentWlan.Count(); i++ )
{
TBuf<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KMaxNameLength> name = currentWlan[i]->Name();
TBuf8<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KWlanBssId> bssid = currentWlan[i]->WlanBssid();
TUint connectionMode = currentWlan[i]->ConnectionMode();
TUint signalStrength = currentWlan[i]->SignalStrength();
TUint securityMode = currentWlan[i]->SecurityMode();
// ...
delete currentWlan[i];
}
currentWlan.Close();
}
delete currentWlanBuf;
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Retrieving information about currently used WLAN using a connection specific
connection ID:
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
TUint connectionCount( 0 );
TUint subConnectionCount( 0 );
TUint connectionId( 0 );
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Get connection count
monitor.GetConnectionCount(
connectionCount,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
if ( connectionCount == 0 ) { /* No connection */ }
// Get connection info (1st connection)
TInt error = monitor.GetConnectionInfo(
1,
connectionId,
subConnectionCount );
if ( error != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Buffer for WLAN information, need space for only 1 WLAN
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg* currentWlanBuf =
new( ELeave ) CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg( 80 );
TPtr currentWlanPtr( currentWlanBuf->Buf()->Des() );
// Get info for currently used WLAN
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
connectionId,
0,
KWlanCurrentNetwork,
currentWlanPtr,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() == KErrArgument ) { /* Bad connection ID or bearer was not WLAN */ }
else if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
else
{
// Process the results
RConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArray currentWlan;
currentWlanBuf->UnpackToL( currentWlan );
// With KWlanCurrentNetwork and no errors, both should be 1
TUint totalAmount = currentWlanBuf->Buf()->Des()[0];
TUint bufferAmount = currentWlanBuf->Buf()->Des()[1];
if ( bufferAmount == 1 )
{
TBuf<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KMaxNameLength> name = currentWlan[0]->Name();
TBuf8<CConnMonWlanNetwork::KWlanBssId> bssid = currentWlan[0]->WlanBssid();
TUint connectionMode = currentWlan[0]->ConnectionMode();
TUint signalStrength = currentWlan[0]->SignalStrength();
TUint securityMode = currentWlan[0]->SecurityMode();
// ...
delete currentWlan[0];
}
currentWlan.Close();
}
delete currentWlanBuf;
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
CConnMonWlanNetworksPtrArrayPckg
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
KErrArgument
-
KErrNotFound
-
KWlanNetworks
-
aConnectionId
KWlanProbeRawBuffers attribute
Used with
GetPckgAttribute()
. Parameter
aConnectionId
must
be a valid connection ID for an existing WLAN connection, or the bearer specific
connection ID
EBearerIdWLAN
.
This attribute is used to perform a broadcast WLAN scan and retrieve the
beacon frames for found WLANs. The information is transferred through a package
(see
CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffersPckg
). The package class
has a buffer that the client needs to allocate memory for. The buffer is filled
with WLAN beacon frames in no specific order, until all frames are entered,
or the buffer runs out of space. The buffer also contains the total amount
of available WLANs and the amount of beacon frames that fit inside the buffer.
The size of a beacon frame is usually somewhere between 60 and 300 bytes.
It consists of a fixed length header and a variable length body.
The beacon frame header structure:
-
2 bytes: Frame control.
-
2 bytes: Duration.
-
6 bytes: Destination address.
-
6 bytes: Source address.
-
6 bytes: BSSID.
-
2 bytes: Sequence control.
-
8 bytes: Timestamp.
-
2 bytes: Beacon interval.
-
2 bytes: Capability information.
-
Body.
This gives 36 bytes and body.
The beacon frame body consists of a sequence of information elements (IE).
The IE structure:
-
1 byte: Information element ID.
-
1 byte: Information element length x (in bytes, max. 255, can be 0).
-
x bytes: Information element data.
This gives x+2 bytes per IE.
#include <rconnmon.h>
RConnectionMonitor monitor;
TRequestStatus status;
monitor.ConnectL(); // Open RConnectionMonitor object
// Buffer for WLAN beacon frame information
CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffersPckg* wlanBeaconsBuf =
new( ELeave ) CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffersPckg( 4096 );
TPtr8 wlanBeaconsPtr( wlanBeaconsBuf->Buf()->Des() );
monitor.GetPckgAttribute(
EBearerIdWLAN,
0,
KWlanProbeRawBuffers,
wlanBeaconsPtr,
status );
User::WaitForRequest( status );
if ( status.Int() != KErrNone ) { /* Error */ }
// Amount of WLAN networks found
TUint totalAmount = wlanBeaconsBuf->Total();
// Amount of beacon frames that fit inside the buffer
TUint bufferAmount = wlanBeaconsBuf->Count();
RConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffersPtrArray wlanBeaconsPtrArray;
wlanBeaconsBuf->UnpackToL( wlanBeaconsPtrArray );
for ( TInt i = 0; i < wlanBeaconsPtrArray.Count(); i++ )
{
CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffer* beacon( wlanBeaconsPtrArray[i] );
TInt beaconLength = beacon->RawBuffer()->Length();
TInt ieCount = 0; // Number if IEs
TInt ieId = 0;
TInt ieLength = 0;
// Header is 36 bytes, body (Information Elements) starts at position 36
TInt index = 36;
while ( index < beaconLength )
{
ieCount++;
ieId = beacon->RawBuffer()->Des()[index++];
ieLength = beacon->RawBuffer()->Des()[index++];
index += ieLength;
// ...
}
if ( index != beaconLength ) { /* error */ }
// ...
delete beacon;
}
wlanBeaconsPtrArray.Close();
delete wlanBeaconsBuf;
monitor.Close(); // Close RConnectionMonitor object
Related APIs
-
CConnMonWlanProbeRawBuffersPckg
-
EBearerIdWLAN
-
GetPckgAttribute()
-
aConnectionId
Related APIs
-
RConnectionMonitor::GetPckgAttribute()
Error handling
Connection Monitor Server may return Symbian platform generic error codes, and
it uses them according to the Symbian platform conventions. The following table
contains the most common ConnMon error codes and a likely explanation of the
cause.
|
|
A request was made with an invalid connection ID parameter, or the
connection has already closed.
|
|
KErrCancel
|
A request has been cancelled by the client, and ConnMon completed it
with
KErrCancel
.
|
|
KErrNoMemory
|
There was not enough free memory in the system to complete an operation.
|
|
KErrNotSupported
|
The requested functionality is not supported by ConnMon.
|
|
KErrArgument
|
A request was made with a bad attribute/connection ID combination.
|
Related APIs
-
KErrArgument
-
KErrCancel
-
KErrNoMemory
-
KErrNotSupported
Memory overhead
The memory overhead caused by the usage of the interface is negligible.
It is highest when using WLAN scanning related functionality, about 16 Kbytes
at its peak.
Extensions to the API
Connection Monitor Server API has been designed to be extensible with new
query attributes and notifications without breaking the binary compatibility
in clients. However, it requires that the clients can handle the unrecognized
notifications. That can be done, for example, by ignoring them.
Related APIs
-
MConnectionMonitorObserver
-
RConnectionMonitor
Glossary
Abbreviations
Connection Monitor Server API abbreviations
|
ConnMon
|
Connection Monitor Server
|
|
IAP
|
Internet Access Point
|
|
SNAP
|
Service Network Access Points, a list of IAPs
|
|
UID
|
Unique Identifier
|
Definitions
Connection Monitor Server API definitions
|
ETel
|
Symbian platform Telephony Server
|
|
Connection
|
In this document, connection refers to an IAP level connection. If
two applications have a data connection activated with the same IAP (and therefore
the same network interface), the number of connections is 1. Identified with
a connection ID.
|
|
Subconnection
|
A PDP context within a certain IAP. The existing connection has always
at least one subconnection. Currently valid only in case of GPRS/UMTS. If
secondary PDP contexts are not used, subconnection means almost the same as
connection. Identified with a subconnection ID. Support for sub- connections
is not implemented.
|
|
Client of connection
|
An application using a certain connection. Identified with UID.
|
|
Internal connection
|
An internal connection has been started by an application running in
the phone.
|
|
External connection
|
An external connection has been started by an application running e.g.
in the PC and the phone is used in modem mode.
|
|
IAP availability
|
An IAP is available, if there is an active connection through this
IAP, or there is a possibility to start a connection through this IAP right
away.
|
|
SNAP availability
|
A SNAP is available, if there is any available IAP inside this SNAP.
|
|